Innovation is more than just ideation. Ultimately, innovation is about value creation.
AI has sparked a growing urgency in the concepts that drive innovation as organizations seek to harness its potential to reengineer business processes and redesign business models. The objective is to generate new value across customer experiences, products, services, operations, and societal outcomes. However, integrating intelligent or “smart” capabilities into products and services poses unique challenges beyond technology. Innovation isn’t just about technological advancements; it’s about developing sustainable, scalable, and impactful solutions that address real-world needs. Achieving this level of sustainable innovation requires a strategic combination of Design Thinking, Data Science (AI/ML), Economics, and Cultural Empowerment. These elements lay the groundwork for fostering meaningful change and long-term success.
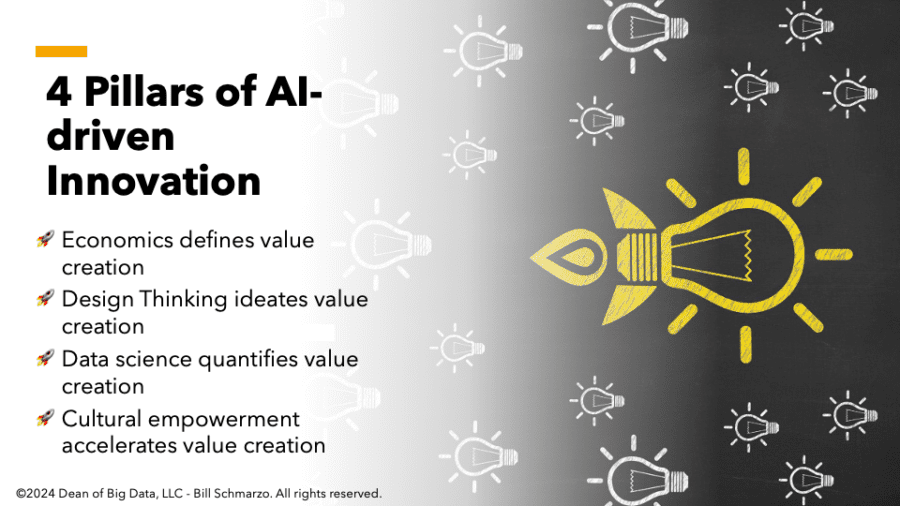
Innovation is the mindset and process of developing new or improved products and services to address unmet market and customer needs.
Do you want to harness the power of AI to achieve new levels of innovation? Organizations must blend four critical pillars to leverage AI to drive new levels of innovation: design thinking, data science, economics, and cultural empowerment. Let’s delve into each of these areas and then provide you with a framework that your organization can use to survive and thrive in this era of AI.
Pillar #1: Design Thinking
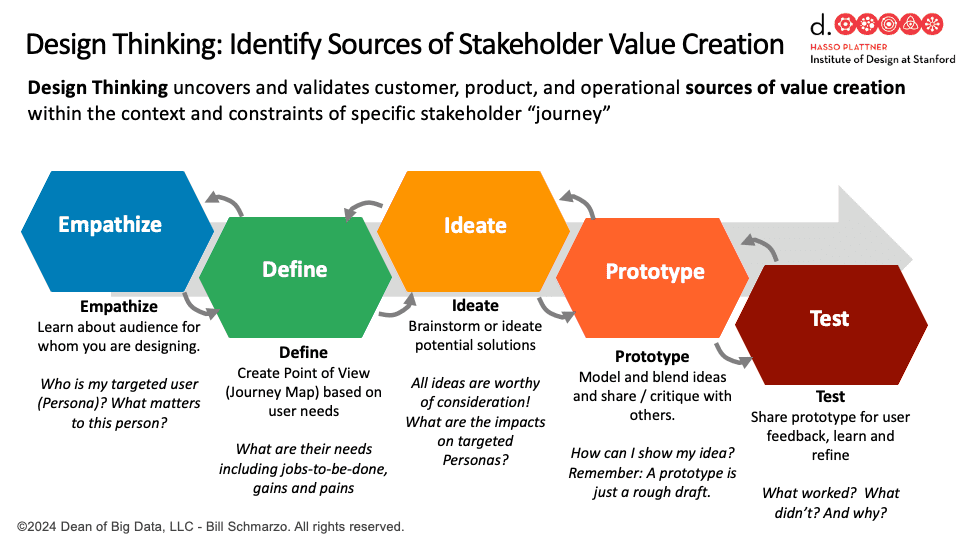
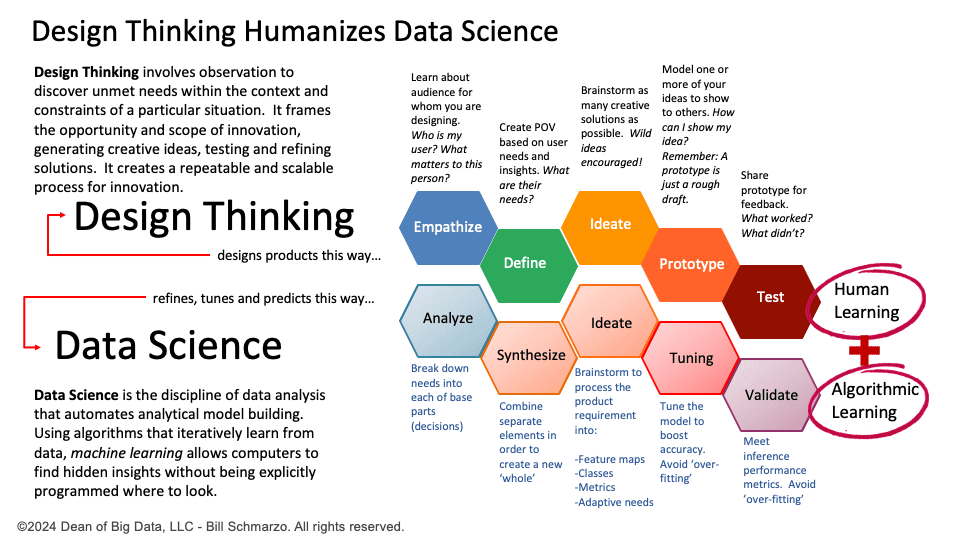
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that focuses on understanding and empathizing with the end-user’s needs. It involves iterative problem-solving, rapid prototyping, testing, and refining ideas based on user feedback. This pillar emphasizes agility, adaptability, and cross-functional collaboration, bringing together diverse perspectives to develop creative and practical solutions. By centering on customer and stakeholder alignment, Design Thinking ensures that innovations are novel but also relevant, effective, and scalable. Fundamental design thinking principles include:
- Agility and Adaptability. Design thinking fosters agility and adaptability by encouraging rapid prototyping, iterative development, and an openness to pivot based on user feedback. This approach enables organizations to quickly respond to evolving customer needs, changing market conditions, and emerging trends. By continuously refining ideas and solutions, teams can stay agile and flexible, ensuring that the innovations they develop remain relevant and impactful.
- Customer-Centricity and Stakeholder Alignment. Design thinking is about customer-centricity and aligning with stakeholder expectations. Solutions are crafted with a deep understanding of the end-user’s needs, pain points, and goals, ensuring that the final product or service is functional and highly relevant to those who use it. By engaging stakeholders early and often in the design process, organizations increase the likelihood of adoption and success by ensuring that all voices are heard and accounted for.
- Continuous Human Learning. A fundamental principle of design thinking is the incorporation of feedback loops and continuous learning. By gathering regular input from users and stakeholders throughout the design process, teams can refine and improve their solutions. These iterative cycles ensure that the solution evolves in alignment with user needs and market dynamics, allowing for ongoing optimization and minimizing the risk of misalignment as conditions change.
Pillar #2: Data Science
Data Science and AI/ML drive innovation by leveraging advanced analytics (AI/ML) to uncover insights, predict trends, and automate processes. This pillar is built on continuous learning, where models improve over time as they adapt to new data and patterns. By using data to make informed, data-driven decisions, organizations can enhance efficiency, optimize resources, and uncover new opportunities for growth and value creation. Key capabilities include:
- Advanced Analytics. Advanced analytics leverage the four types of AI—analytical, Causal, Generative, and Autonomous—to extract valuable insights from vast datasets, uncovering patterns and trends that would otherwise remain hidden. These capabilities enable precise predictions of future outcomes, helping businesses make proactive and informed decisions. Furthermore, autonomous automation can streamline processes by handling repetitive tasks, optimizing operations, and enabling scalability, all while reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Continuous Algorithmic Learning. Continuous learning is the hallmark of AI models, enabling them to adapt and improve over time by processing new data and adjusting to changing patterns. Leveraging technologies like deep learning and reinforcement learning, AI systems refine their predictions and recommendations, becoming more accurate and relevant with each iteration. Feedback loops are critical as they enable AI models to evolve autonomously, ensuring they remain reliable, adaptive, and capable of delivering value, much like the iterative improvement approach seen in design thinking.
Pillar #3: Data-driven Economics
Data-driven economics focuses on understanding and maximizing the economic value of data. Unlike traditional assets that depreciate, data appreciates as it is used across different scenarios, making it a powerful driver for business transformation. This pillar emphasizes the importance of monetization, sustainable ROI, and strategic use of data to create value. By treating data as a reusable asset, organizations can prioritize initiatives that offer the most significant economic impact, ensuring that innovation efforts are financially viable and scalable.
- Economic Value of Data: This pillar emphasizes that data should be considered a strategic asset. Data’s value increases as it is used across multiple scenarios, making it a powerful driver of business transformation and innovation.
- Monetization and Value Creation: Organizations need to focus on how data can drive value, not just in terms of efficiency but also by enabling new business models, services, and revenue streams.
- Sustainability and ROI: Effective data economics ensures that the benefits derived from data and analytics initiatives are sustainable, scalable, and measurable, guaranteeing a clear return on investment.
Pillar #4: Cultural Empowerment
Cultural Empowerment is about creating an environment where data and AI literacy are integral to the organization, enabling employees at all levels to leverage these technologies effectively. This pillar fosters a mindset of continuous learning, experimentation, and collaboration, ensuring that teams are empowered to innovate without fear of failure. Ethics and governance play a critical role in embedding responsible AI practices to build trust and ensure that innovations align with societal values.
- Empowerment Through Education: Building a culture where all employees are AI & Data Literate ensures everyone understands the value of data and their role in leveraging it responsibly. This fosters a more engaged and proactive workforce that can drive innovation from any part of the organization.
- Ethics and Governance: Embedding ethical considerations and robust governance frameworks ensures that innovation aligns with societal values and legal standards, fostering trust and responsible AI development. This is crucial for gaining stakeholder and customer confidence in new technologies.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Cultural empowerment also means creating an environment where learning is constant, failures are seen as opportunities, and people are willing to adapt. This mindset fosters resilience and long-term success.
- Organizational Improvisation and “Team of Teams.” Organizational improvisation fosters adaptability and real-time problem-solving, enabling teams to respond quickly and creatively to unexpected challenges. The “Team of Teams” approach encourages agile, cross-functional collaboration, promoting a shared vision, open communication, and continuous learning for practical innovation at scale.
AI-Driven Innovation and Thinking Like a Data Scientist Methodology
The Thinking Like a Data Scientist (TLADS) methodology captures and activates these four pillars of innovation. By integrating Design Thinking, Data Science, Data-Driven Economics, and Cultural Empowerment, TLADS offers a holistic approach to driving sustainable, responsible, and impactful innovation.
- How TLADS Activates Design Thinking Pillar: TLADS aligns with the principles of Design Thinking by starting with a deep understanding of business needs and customer problems. It emphasizes empathizing with stakeholders, iterative development, and regular feedback loops, ensuring solutions are refined based on real-world input.
- How TLADS Activates the Data Science Pillar: TLADS provides a structured approach to leveraging data science and AI/ML, guiding teams from modeling entities to exploring and refining analytics algorithms. By embedding feedback mechanisms and continuous learning into the process, the methodology ensures that AI models can adapt and improve as new data becomes available.
- How TLADS Activates the Data-driven Economics Pillar: TLADS emphasizes prioritizing and quantifying business use cases to ensure that data initiatives are strategically aligned and deliver measurable economic value. By treating data as a renewable and reusable asset, the methodology helps organizations unleash their data assets’ economic value, driving both immediate gains and long-term sustainability.
- How TLADS Activates the Cultural Empowerment Pillar: TLADS fosters a culture of continuous learning, data literacy, and ethical responsibility, encouraging experimentation, collaboration, and learning from failures. By integrating ethical guidelines and governance into the framework, TLADS ensures that AI initiatives are practical, responsible, and trustworthy.
Organizations that embrace this comprehensive approach to innovation will find themselves better equipped to navigate the complexities of modern business environments, turning data into actionable insights and insights into real-world impact.
Conclusion
The four pillars of AI-driven innovation provide a comprehensive framework for driving sustainable and responsible innovation. This approach ensures that innovation is human-centered, data-driven, economically sound, and culturally empowered, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of modern business environments effectively.
With these four pillars, organizations can establish a robust foundation to harness the full potential of data and AI while being agile, ethical, and strategically aligned. This will drive immediate innovation and build the capability to evolve and adapt continuously in the face of future challenges.
