This article was written by Adit Deshpande on his own blog.
This is the 3rd installment of a new series called Deep Learning Research Review. Every couple weeks or so, I’ll be summarizing and explaining research papers in specific subfields of deep learning. This week focuses on applying deep learning to Natural Language Processing. The last post was Reinforcement Learning and the post before was Generative Adversarial Networks ICYMI
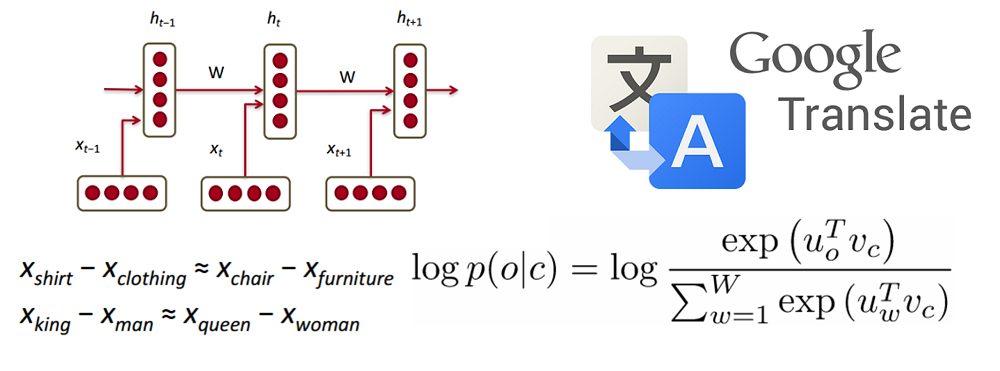
Introduction to Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is all about creating systems that process or “understand” language in order to perform certain tasks. These tasks could include
- Question Answering (What Siri, Alexa, and Cortana do)
- Sentiment Analysis (Determining whether a sentence has a positive or negative connotation)
- Image to Text Mappings (Generating a caption for an input image)
- Machine Translation (Translating a paragraph of text to another language)
- Speech Recognition
- Part of Speech Tagging
- Name Entity Recognition
The traditional approach to NLP involved a lot of domain knowledge of linguistics itself. Understanding terms such as phonemes and morphemes were pretty standard as there are whole linguistic classes dedicated to their study. Let’s look at how traditional NLP would try to understand the following word.
To read the full article, click here.
- Invitation to Join Data Science Central
- Free Book: Applied Stochastic Processes
- Comprehensive Repository of Data Science and ML Resources
- Advanced Machine Learning with Basic Excel
- Difference between ML, Data Science, AI, Deep Learning, and Statistics
- Selected Business Analytics, Data Science and ML articles
- Hire a Data Scientist | Search DSC | Classifieds | Find a Job
- Post a Blog | Forum Questions
