5G is critical to many business applications.
Below is a great free opensource book to get started with 5G.
But first, here are five reasons why you should study 5G
Private 5g
If you want to deploy broadband within the Enterprise – there are two main options: rely on WiFi or work with the public telecom networks.
These choices exclude many applications which need seamless, business critical connectivity and are deployed within a specific locality – for example factories, warehouses, schools, airports, hospitals, buildings and conference venues.
For such applications, we need both simplicity of WiFi networks (which do not scale up) and the reliability of public telecoms networks(which do not scale down).
Private 5G offers a new option by providing a network that provides the reliability and coverage of public cellular with the simplicity and affordability of WiFi
Private 5G is a component of 5G deployments that can deliver low latency and high bandwidth connectivity within enterprise campus. Because the network is effectively managed by the enterprise, the data is secure and private.
IoT local area and wide area networks
5G is the missing link for IoT and Edge applications. According to Frost & Sullivan, edge computing in wireless networks would grow from a $64.1 million business in 2019 to a $7.23 billion business in 2024. 90% of industrial enterprises will use edge computing by 2022. This trend can only be accelerated by the pandemic especially post lockdown.
Telemedicine – remote medicine
5G networks enable many telemedicine applications especially those that need video or high bandwidth. These include transferring large files, remote consultations through video, Augmented reality and virtual reality
5G and the Cloud
The Cloud enables the allocation of resources dynamically as per the needs of applications. Cloud native computing is a software development approach that utilizes cloud computing to create and deploy scalable applications. Cloud native applications are enable the creation of loosely coupled systems that are resilient. Telecoms Operators are deploying their own cloud platforms and at the same time, they are also partnering with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP and IBM to provide on demand infrastructure resources such as compute, network and storage.
5G and the Future of work
5G will play a key part in the future of work post pandemic and will enable behaviours like remote work, online education and entertainment.
The book is 5G Mobile networks: A systems approach co-authored by Larry Peterson – Princeton University Computer Science professor
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Standardization Landscape
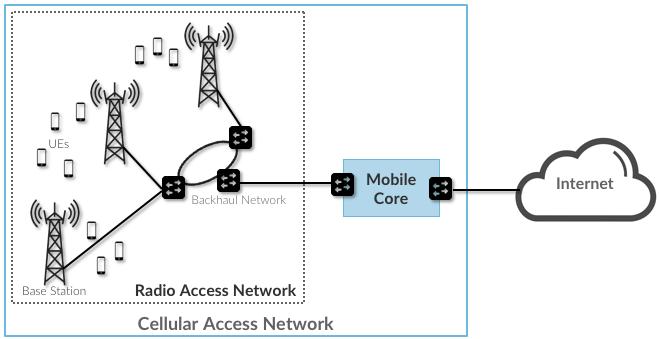
1.2 Access Networks
1.3 Edge Cloud
Chapter 2: Radio Transmission
2.1 Coding and Modulation
2.2 Scheduler
2.3 New Radio (NR)
Chapter 3: Basic Architecture
3.1 Main Components
3.2 Radio Access Network
3.3 Mobile Core
3.4 Security and Mobility
3.5 Deployment Options
Chapter 4: RAN Internals
4.1 Packet Processing Pipeline
4.2 Split RAN
4.3 Software-Defined RAN
4.4 Architect to Evolve
Chapter 5: Advanced Capabilities
5.1 Optimized Data Plane
5.2 Multi-Cloud
5.3 Network Slicing
Chapter 6: Exemplar Implementation
6.1 Framework
6.2 Platform Components
Chapter 7: Cloudification of Access
7.1 Multi-Cloud
7.2 EdgeCloud-as-a-Service
7.3 Research Opportunities
Image source 5G Mobile networks: A systems approach
