Introduction
The boundaries of the enterprise are becoming diffused. You have data on the network, on the endpoint, and on the cloud. Enabling visibility into your data flows is a critical first step to understanding which data is at risk for theft or misuse. You need to know what data you have, where it’s located, and why that data exists in order to properly protect it. This is where data discovery and data classification come into play.
Data Discovery is an important foundation to gain that knowledge of the what, where, and why of your data. Data Classification allows you to create a scalable security solution. Such solutions as file tagging can be used across platforms from Windows to Mac and also enables you to tag files across the endpoint, network and cloud. This, in turn, gives you visibility into data across all of your infrastructures so you can apply the appropriate policies. Hence,
What is Amazon EMR and Apache Atlas
Amazon EMR is a managed cluster platform that simplifies running big data frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, on AWS to process and analyze vast amounts of data. By using these frameworks and related open-source projects, such as Apache Hive and Apache Pig, you can process data for analytics purposes and business intelligence workloads. Additionally, you can use Amazon EMR to transform and move large amounts of data into and out of other AWS data stores and databases, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and Amazon DynamoDB.
Apache Atlas is the one-stop solution for data governance and metadata management on enterprise Hadoop clusters. Atlas has a scalable and extensible architecture which can plug into many Hadoop components to manage their metadata in a central repository. In this blog, we are going to look on one such data discovery and classification tool i.e Apache Atlas. For further use, we will be using Apache Atlas on Amazon EMR. Let us look at more features of Apache Atlas at our disposal!
Apache Atlas Features
1. Centralised Metadata Store
Atlas provides true visibility in Hadoop. By using the native connector to Hadoop components, Atlas provides technical and operational tracking enriched by business taxonomical metadata. Atlas facilitates easy exchange of metadata by enabling any metadata consumer to share a common metadata store that facilitates interoperability across many metadata producers
2. Data Classification
Ability to dynamically create classifications — like pii, expires_on, data_quality. Classifications can include attributes — like an expiry_date attribute in EXPIRES_ON classification. Entities can be associated with multiple classifications, enabling easier discovery and security enforcement. Propagation of classifications via lineage — automatically ensures that classifications follow the data as it goes through various processing.
3. Data lifecycle Management
It leverages existing investment in Apache Falcon with a focus on provenance, multi-cluster replication, data set retention and eviction, late data handling, and automation.
4. Centralised Security
Fine-grained security for metadata access, enabling controls on access to entity instances and operations like add/update/to remove classifications. Integration with Apache Ranger enables authorization/data-masking on data access based on classifications associated with entities in Apache Atlas. Integration with HDP security that enables you to establish global security policies based on data classifications and that leverages Apache Ranger plug-in architecture for security policy enforcement.
The Architecture of Atlas
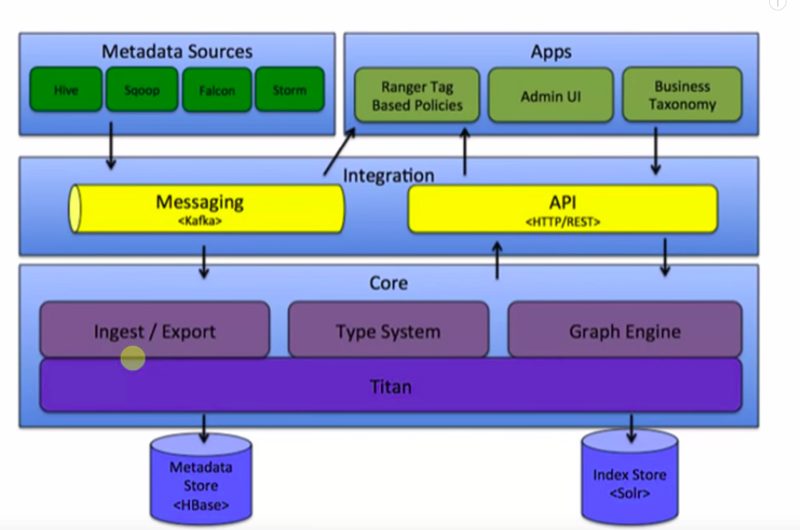
This is the basic structure of how this Atlas work. It has got a core component for ingestion and export. In the back-end, it’s using the HBase database for metadata store. It also requires a solar okay that is for index and again the between the different components, the message passing is through Kafka. It can connect Atlas with REST API calls. Also, we have an admin console to manage and monitor all the operations. So, this is a core structure of Atlas and as we know now that it requires HBase hence before we do the installation of Atlas so we need to have a working HBase instance running. Also, we need a SOLAR incensed.
Amazon EMR–Apache Atlas Workflow
To demonstrate the functionality of Apache Atlas, we will be doing the following in this post:
- Launch an Amazon EMR cluster using the AWS CLI or AWS Cloud Formation
- View the data lineage of a hive table
- Create a classification
- Discover metadata using the Atlas domain-specific language
Step 1: Launching Amazon EMR and Atlas
Now, we will be looking into running atlas on Amazon EMR. I have one cluster running on Amazon AWS as a single node instance I have installed Atlas and all its pre-required components like HBase and Kafka beforehand.
Now, we can open Atlas window by clicking Atlas. Default credentials are admin as username and admin as password. Once you are able to log in successfully, you will be on Atlas page
Once, we are logged into Atlas, we can see a couple of tabs available right in front. They are tags, taxonomy and search.
The tag is nothing but a way of grouping certain objects say for example we have PII tag (personally identified information). We can add this tag to certain databases tables or column wherever we need it. Through tags, by using a Ranger, we can control the access of these objects
In the search page, we have two options text-based search or DSL. DSL stands for a domain-specific language. It is similar to SQL kind of a query. You can use similar queries and get the details. By default, there are a lot of data sources you can connect to. We will select hive DB here. Once selected, it will show all the hive databases available. Furthermore, we can create a few more databases which will get listed here.
Step 2: Viewing Data Lineage
Data lineage is defined as a data life cycle that conveys data origin and where data moves over time. In Apache Hive, if I create a table (TableA) and then insert data (from another table TableB), the data lineage will display TableA as the target and Table B as the source/origin. These two tables are linked together by a process “insert into Table..”, allowing a user to understand the data life cycle. In a Hadoop ecosystem, Apache Atlas contains the data lineage for various systems like Apache Hive, Apache Falcon and Apache Sqoop.
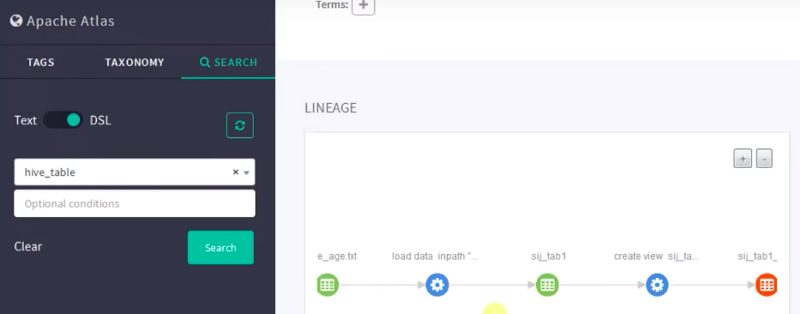
Data lineage is one of the most important features of Apache Atlas. If we click any table or view the table, we can see how the data is flowing. In simple terms, we will get a history of data flow.
In the above pic, we have an initial file. I created a table on Hive and loaded the values into it from a text file. We can easily see this data upload process in the first two nodes. After the data load, we placed all the data into the table “sij” underscore. After that, we made a view of that table.
You can see a much more complex data lineage in the image below
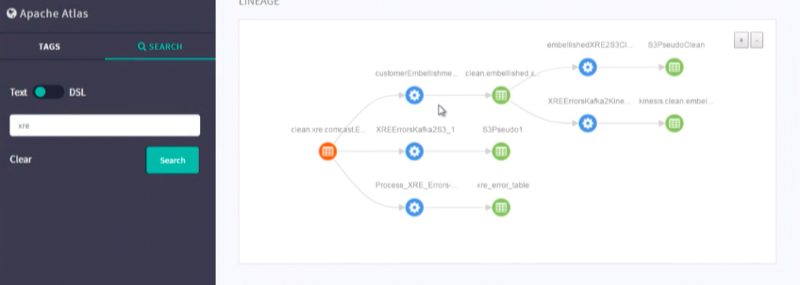
In short, this is a data lineage which Apache atlas provides us and this is how you can get the lineage.
Step 3: Creating a Classification
Classification propagation enables classifications associated with an entity to be automatically associated with other related entities of the entity. This is very useful in dealing with scenarios where a dataset derives its data from other datasets — like a table loaded with data in a file, a report generated from a table/view, etc. For example, when a table is classified as “PII”, tables or views that derive data from this table (via CTAS or ‘create view’ operation) will be automatically classified as “PII”.
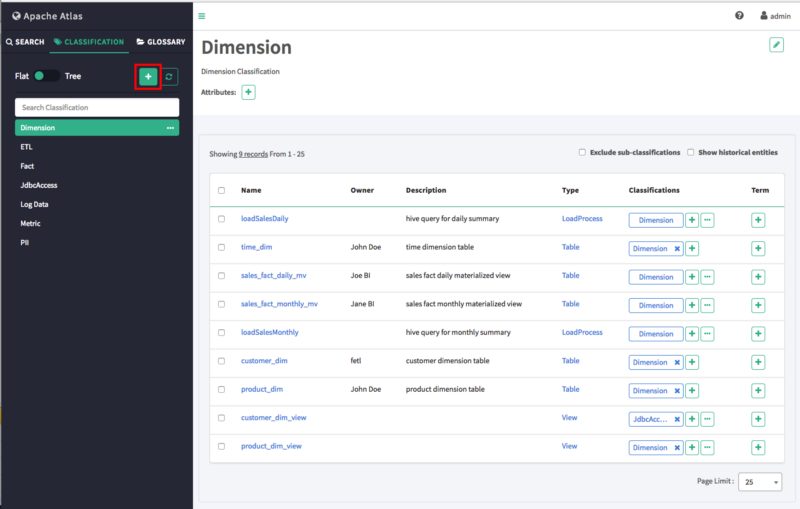
On the Atlas web UI, click CLASSIFICATION, then click the + icon.
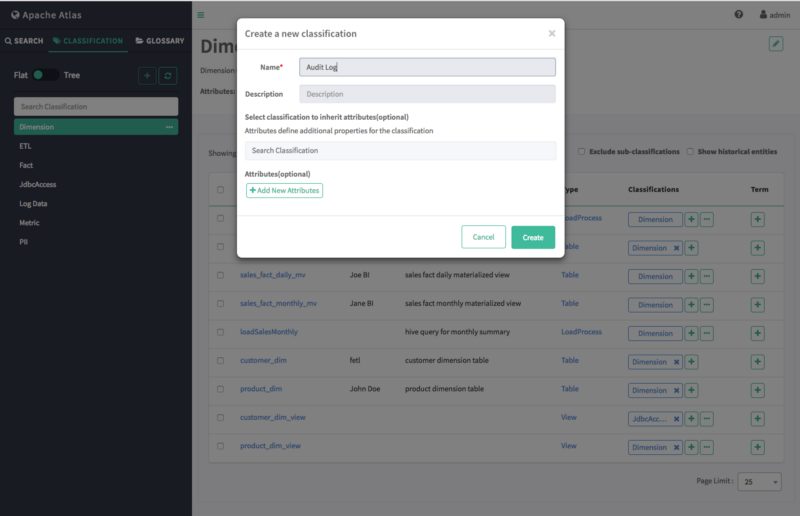
On the “Create a new classification” pop-up, type in a name and an optional description for the classification. You can use the Select classifications to inherit attributes box to inherit attributes from other classifications. Click Add New Attributes to add one or more new attributes to the classification. Click Create to create the new classification.
The new classification appears in the Classifications list.
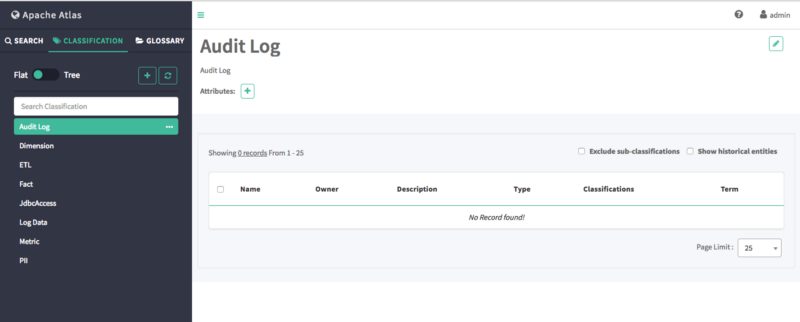
Step 4: Using DSL for Discovering Metadata
Atlas DSL (Domain-Specific Language) is a SQL like a query language that enables you to search metadata using complex queries. In the search tab, you have two options of searching through the databases. One is normal text search and the other is DSL search.
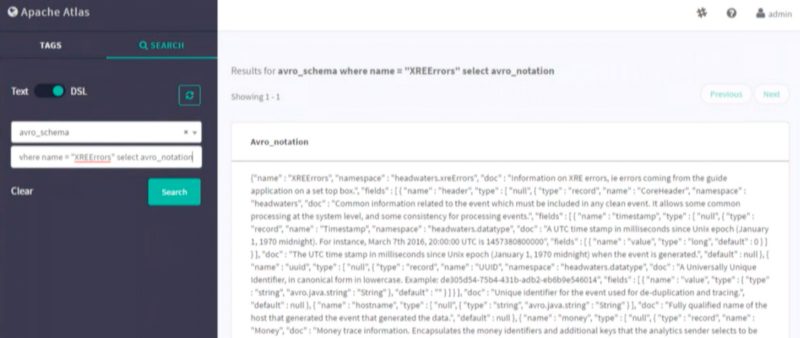
After selecting the DSL search, we can use SQL like queries to extract information out from the tables present in our HIVE database. In the optional, conditions input we can write our SQL queries. We wrote one such query here to extract all the error logs in a specific format. In the image below, you can see results
Summary
In this article, we focused on Apache Atlas as an example to explain and demonstrate metadata management in enterprise governance. We had a look at important topics like data lineage, data discovery, and classification. Apache Atlas is one of the prime tools handling all the metadata management tasks and has a lot of future prospects.
Read more here
