Around two decades ago, marketing existed as a soft function within organizations. There is no denying its importance, of course, but from an organizational perspective, it was a function hard to measure in terms of impact on the bottom-line. But then boomed the digital age, and with it, an advent of channels that came to be known as social media. And in its wake, followed big data – a subject that requires little explanation.
What does this mean? In simple terms, marketing is now being increasingly treated as a hard science that does indeed impact the bottom-line. It has pushed marketers out of conventional roles into territories of social media, digital campaigns, tactics for personalization, and customer analytics.
The clock on marketing is shifting once more, however, and it’s because of the much talked about emerging trend – artificial intelligence.
What has Changed in Marketing?
Marketing is a broad term and could be categorically broken down into functions such as marketing analytics, research, content and creative development, customer service, social media, public relations, and operations. You could call it the marketing standard for today, meaning organizations rely on the expertise of different people within these fields.
But in a rapidly-developing world, where technology and innovation move at an aggressive pace, organizations are better placed when scalability becomes part of the overall strategy. When dependent on manpower alone, scalability comes in strung with other factors – talent acquisition, cultural fitment, and infrastructural costs among many others.
Both human expertise and the need to scale are important aspects of organizational success and growth. On a finer scale, this would extend to marketing success also. But let’s look at why that is.
- Data: An innumerable amount of data is amassed annually by organizations worldwide. While data scientists and analysts are essential to deriving meaningful insights from this data, machines possess the inherent ability to process information at a faster pace, by the millions.
- Virtual Workforce: By 2022, 40% of customer-facing organizations are likely to use a virtual support agent to assist with decision-making and process support. There’s also a prediction about one in five people in developed economies using virtual assistants for their day-to-days. These stats are both from Gartner.
- Voice & Visual Interaction: Voice and visual interaction at a virtual level is what marketing shifts to in a digital era. Response time, ease of communication, and more play into the market for virtual assistance, which is expected to become an influential mode of brand interaction and purchase in the coming years.
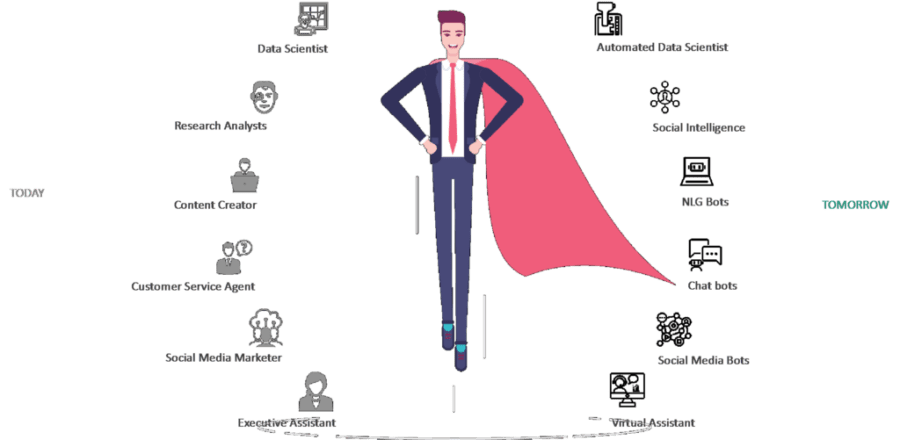
What this suggests is that Chief Marketing Officers are becoming more convinced of the strategic impact of artificial intelligence on their overall marketing strategy. It opens an opportunity to massively scale without the problems associated with a human workforce. A residual impact is also the elimination of certain job roles, which are better and more efficiently handled by machines.
How Can You Get Started with AI?
Success with artificial intelligence is determined by the availability of the right data, implementation, and use cases. Build confidence within the organization about the approach by first addressing business-critical use cases that are inherently less complex. Here are some factors to consider when implementing an AI strategy:
- Augmented Data Discovery & Machine Learning: With ever-increasing data assets, marketers would need to find an effective means to strategize and analyze these assets. By design, these platforms could help marketers with rapid, real-time insights for them to act upon.
- Chatbot & Virtual Assistant (VA) Strategy: Customers are now increasingly interacting with brands and enterprises via VAs or chatbots. The optimization of digital assets is necessary to enable and enhance customer experience on scale. As a next step, marketers might even need to train and become VA-ready – utilizing assistants for analytics, machine learning, customer service, personalization, and more.
- Voice & Visual Factor: Digital assets such as websites, eCommerce portals, social media pages, and more could become focal in implementing an AI strategy – meaning that it is essential to arm them through both voice and visuals. Speech analytics can also help by understanding consumer behavior based on the pattern of interaction.
Marketing teams would become smaller, but trend upward in terms of relevance and efficiency. This would incite a change in the conventional definition of marketing as well, leaving today’s marketers with the choice to either upskill or fade into irrelevancy. It’s important to stress this point, because artificial intelligence isn’t a technology designed to replace humans in their entirety. A wiser take on the matter would be in calling it a power-up for the everyday marketer – an augmentative technology.
For example, while it is true that these technologies may extract actionable insights rapidly from data assets, the decision-making process remains mostly human. Remember, artificial intelligence and machine learning serve better as a part of the overall strategy than standalone strategies that other marketing goals revolve around.
Here are a couple of stellar benefits to consider:
- Smarter Approach to Marketing: The rise of cognitive technologies, such as Automated Machine Reasoning, Machine Learning, and Natural Language Processing & Generation, could open doors for large amounts of data to be analyzed without any form of manual intervention. Data is collected at a faster rate and is processed into actionable insights just as speedily.
- Improved Efficiency: It goes without saying that efficiency is a by-product of all cognitive technologies used for automating manual processes. This is in addition to activities that might require higher order cognitive involvement. Some interesting examples to look at are automated report generation, content curation or creation, and sales candidate scoring.
- Predicting the Customer Journey: This is an important aspect for marketing – to predict and act depending on the various stages of the customer journey. Machine Learning and Deep Learning could help marketers make pointed and accurate decisions based on a customer’s journey, enabling the delivery of all the right offerings at the right intervention points. Data could be gathered from several connected devices such as smart watches, mobiles, and more.
- Speed to Improvisation: Continuous improvisation is an essential recipe for success. AI and Cognitive Systems thrive on that feature. By self-learning, these systems can adapt to customer sentiment in real-time and reflect those changes in reports for marketers to utilize.
Marketing is changing at its very foundation, and for the better. It’s become easier, smarter, and a measurable investment. As the second decade of the 21st century comes to an end, organizations and marketers alike now stand at the precipice of this change. It’s a choice, yes. But one that might decide your chances at success in this new era. So, what will it be?
Practice Head, BI, Data Science, and Big Data at Marlabs Inc.
As an experienced Data Science practitioner, Senthil Nathan R has executed several BI and Data Science projects across the globe. Heading the product management function at data analytics firms, he has led large teams of big data and data science professionals. Machine learning is an area of special interest to Senthil. He was instrumental in conceptualizing and launching “Smart Machine Insights” – an automated machine learning platform similar to IBM’s Watson. Another solution that Senthil created was a big data-based mobile social network analysis solution that won numerous accolades and was featured in the NASSCOM product excellence matrix for Analytics. Customer experience management and analytics is another area where Senthil has consulted with several clients.

