In part 1 of the series “A Different AI Scenario: AI and Justice in a Brave New World,” I outlined some requirements for the role that AI would play in enforcing our laws and regulations in a more just and fair manner and what our human legislators must do to ensure that outcome.
In part 2, I discussed a real example of how AI is being used to enforce our laws and regulations more unbiased, consistent, and transparently – robot umpires – and what we can do to humanize those robot umpires (and AI) just a little. I also tapped some time-tested standards that courts use to guide the admissibility of evidence and how those lessons can help us build more fair and just AI models in this brave new world of AI.
Let’s bring it all together with a robust conversation about operationalizing the AI governance necessary to ensure that our AI models deliver more meaningful, relevant, responsible, and ethical outcomes. And introduce the AI Model Trail concept as a way to verify and validate AI model compliance.
AI Model Governance
The success of this AI laws and regulations enforcement scenario is based upon an open, unbiased, and transparent AI model governance system. An effective AI model governance is the bedrock for ensuring the fairness, equity, and ethics of the AI models used to enforce the laws and regulations and for building the trust and confidence of the public and the policymakers in the AI models.
AI model governance involves multiple and diverse stakeholders, such as the AI developers, the AI users, the AI regulators, and the AI beneficiaries, who have different roles, responsibilities, and interests in the AI models. AI model governance covers the entire AI lifecycle, from the design and development to the deployment and maintenance to the ongoing evaluation and improvement of the AI models. AI model governance requires a combination of methods and tools, such as documentation, explanation, feedback, correction, and redress, to provide transparency, accountability, and oversight for the AI models.
Some of the most essential factors for AI model governance success in the eyes of the average citizen are:
- The alignment of the AI models with the human-defined laws and regulations and the ethical, social, and legal norms and standards that govern the AI models’ domain and application.
- The quality and reliability of the data, algorithms, parameters, and metrics that the AI models use to make their decisions, and the validation and verification of their accuracy, relevance, and reliability.
- The performance and impact of the AI models and the measurement and assessment of their effectiveness, efficiency, and fairness, as well as their potential or actual errors, harms, or impacts.
- The public and policymakers’ participation and involvement in the AI model governance process and soliciting and incorporating their feedback, input, and preferences.
- The public and policymakers’ awareness and education about AI’s current and future state, its implications and challenges, and the provision and dissemination of understandable and verifiable information about the AI models.
Monitoring AI Model Governance: AI Model Audit Trail Concept
One way to ensure trusted and effective AI Governance is to mandate that all AI models generate an AI Model audit trail that captures the AI models’ metrics and variable and their respective weights at the time of any decision or action. The audit trail would provide the basis to validate and certify the AI models’ performance. AI certification models could be developed by government and independent agencies, such as GDPR, CCPA, or ACLU, to ensure that the AI models follow the laws and regulations and respect the rights and freedoms of the data subjects and natural persons.
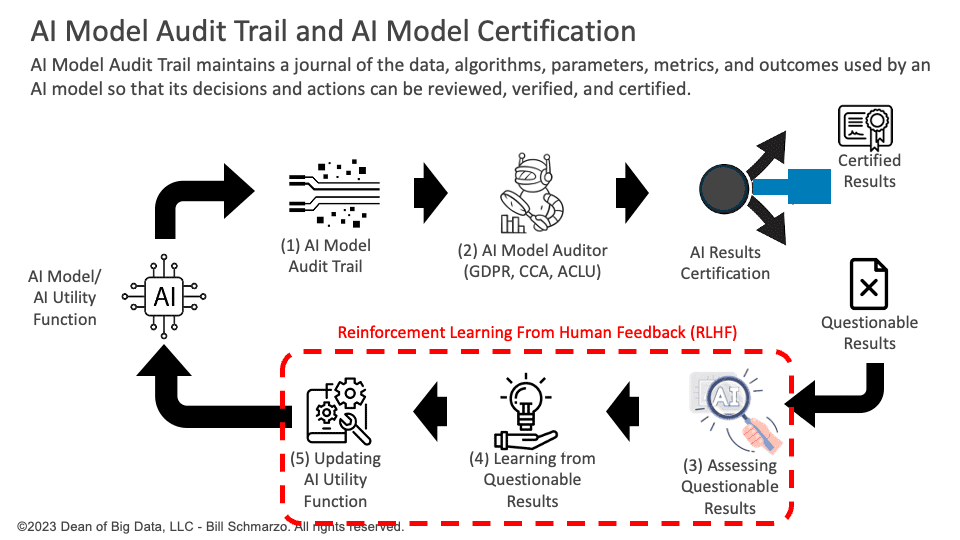
Figure 1: AI Model Audit Trail Concept
The AI Model Audit Trail process is the idea of creating and maintaining a record of the data, algorithms, parameters, metrics, and outcomes that an AI model uses to perform its tasks or make its decisions to provide transparency, accountability, and quality for the AI model and its users, stakeholders, and regulators.
The steps that comprise the AI Model Audit Trail process are:
- The AI model generates an audit trail that creates a snapshot of each decision or action’s data, algorithms, parameters, and metrics. This step involves capturing and storing the relevant information and metadata used or produced by the AI model at each point of its operation, including the input and output data, the algorithm and parameter settings, the metrics and indicators, and the outcomes and impacts of the AI model’s decisions or actions.
- Independent AI Model Auditors (GDPR, CCA, ACLU) analyze the audit trail to verify that the actions and related outcomes were unbiased, fair, and ethical. The AI Model Auditor checks the accuracy, relevance, and reliability of the data, algorithms, parameters, and metrics and the effectiveness, efficiency, and fairness of the outcomes of the AI model’s decisions.
- A human auditor would analyze the outcomes and the AI model operational snapshot for questionable results. This step involves investigating and resolving any issues or disputes that arise from the AI model’s decisions using various methods and tools, such as forensics, analytics, or simulation. The human auditor would make a final judgment or determination on the validity, acceptability, or appropriateness of the AI model’s decisions or actions and the responsibility or liability of the AI model or its creators or users.
- The AI model learnings from the human auditor are captured, documented, and quantified, and any regulatory fines are assessed. The AI model learnings should include the errors, harms, or impacts that the AI model caused or could cause and the corrections, improvements, or mitigations the AI model needs or could benefit from.
- The AI model learnings are fed back to update the AI Utility Function to ensure these inequities do not happen again. The AI Utility Function should be updated to reflect the changes or adjustments in the data, algorithms, parameters, or metrics used or produced by the AI model and align with the desired outcomes and objectives that the AI model aims to achieve or produce.
Some of the benefits of the AI Model Audit Trail concept are:
- Improve AI model transparency and accountability by providing a traceable and verifiable record of their decisions and enabling the inspection of their behavior and performance.
- Enhance the quality and reliability of the AI models by ensuring that they use appropriate data, algorithms, parameters, and metrics and by verifying their accuracy, relevance, and reliability.
- Promote AI model fairness and ethics by assessing and certifying their compliance and ethics and identifying and correcting any biases, errors, or harms they may cause.
AI Model Audit Trail Challenges
We must address several challenges to make the AI Model Trail concept work. Here is a matrix that summarizes the challenges and the actions for using AI model audit trails and AI certification AI models to drive trusted and effective AI governance.
| AI Model Audit Trail Challenges | AI Model Audit Trail Solutions |
| It is technically challenging as it requires the integration of various data sources, algorithms, parameters, and metrics and developing and maintaining robust AI certification AI models. | – Use common data formats, protocols, and standards to facilitate the integration and standardization of the data sources, algorithms, parameters, and metrics. – Use modular, scalable, and reusable AI certification models that can be easily adapted and updated to different scenarios and contexts. |
| Legally or socially controversial, as it would involve the collection and processing of personal or sensitive data, and the application and enforcement of different or conflicting laws and regulations, and the balancing of different or competing values and interests. | – Use privacy-preserving techniques to protect personal or sensitive data from unauthorized access or misuse. – Harmonize regulatory frameworks to ensure the compliance and consistency of the AI certification AI models across different jurisdictions and domains. – Use stakeholder engagement methods to elicit and incorporate different perspectives in AI certification AI models. |
| Ensuring the trustworthiness of the AI models will require the full complexity and context of the AI models’ behavior and account for the model’s trade-offs, uncertainties, or risks involved in the AI models’ optimization process. | – Use explainable AI techniques to provide evidence for the AI models’ decisions and their underlying logic and reasoning. – Use reliable AI techniques to measure the trade-offs, uncertainties, or risks in the AI models’ optimization process. – Use feedback and correction mechanisms to enable regulators to monitor, evaluate, and improve the AI models’ performance and address any related errors, harms, or impacts. |
Table 1: AI Model Audit Trail Challenges and Actions
Summary: Create a More Fair, Just, and Empowered Society – Part 3
Part 3 continued the “AI and Justice in a Brave New World” conversation by discussing the AI governance necessary to ensure that our AI models deliver more meaningful, relevant, responsible, and ethical outcomes. We shared the AI Model Audit Trail concept and how third parties could create AI certification models that ensure that the AI models follow the laws and regulations and respect the rights and freedoms of the data subjects and natural persons. Finally, we outlined the challenges to the AI Model Audit Trail concept and the steps we can take to ensure its viability.
I will have one more blog – a summary – that brings together this entire series on the eight steps to deliver on the promise and potential of creating a more fair, just, and empowered society with AI.
